Interfaces :
- Interfaces are pure abstract classes (100 %) and are similar to classes.
- An interface cannot be instantiated, meaning you cannot create an instance of an interface.
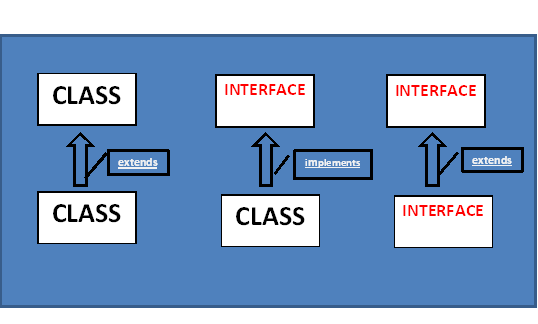
- It can be implemented by a class or extended by another interface.
- Interfaces are used to achieve complete abstraction in java.
Syntax :
interface
interface_name {
}
Example of interface :
public interface DriveCar {
void
turnLeft();
void
turnRight();
void moveBack();
void accelerate();
}
The above
is equivalent to :
public interface DriveCar {
public
abstract void turnLeft();
public
abstract void turnRight();
public
abstract void moveBack();
public
abstract void accelerate();
}
Rules for
using Interface:-
- Methods inside interface must be static, final, native or strict fp.
- All variable declared in interface are implicitly public, static and final (Constants).
- All methods are public and abstract by default, Even if you don’t use the keywords (Therefore 100 % abstract).
- Interface cannot implement a class.
- Interface can extend one or more interfaces.
- Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance, but a class can implement more than one interface.
- Interface must implement all the methods in its class.
Example program 1 :
package
org.javanoobs.interfaces;
public interface Movable {
void move();
}
package
org.javanoobs.interfaces;
public class Vehicle implements Movable{
public void move(){
int avgSpeed = 40;
System.out.println(" Average
speed is : " +avgSpeed);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Vehicle
vh = new Vehicle();
vh.move();
}
}
Output :
Average speed is :
40
Example program 2:
package
org.javanoobs.interfaceinheritance;
// This is the first interface.
public interface Movable {
boolean isMovable();
}
package org.javanoobs.interfaceinheritance;
// this is the second interface.
public interface Rollable {
boolean isRollable();
}
package
org.javanoobs.interfaceinheritance;
public class Tyre implements Movable,Rollable {
int width;
public boolean isMovable(){
System.out.println(" This is
inside of isMovable method... ");
return true;
}
public boolean isRollable(){
System.out.println(" This is
inside of isRoallable method ");
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Tyre
tr = new Tyre();
System.out.println(tr.isMovable());
System.out.println(tr.isRollable());
}
}
Output
:
This is inside of isMovable method...
true
This is inside of isRoallable method
true

No comments:
Post a Comment